Gabillon Model
SDE
\[dF(t,T_i) = F(t,T_i)\left(e^{-k(T_i-t)} \sigma_s(t,T_i) d W_s(t) + \left(1- e^{-k(T_i-t)}\right) \sigma_l d W_l(t)\right)\] \[E(dW_s(t)dW_l(t)) = \rho dt\]Calibration
There are two part of model parameter fitting. Firstly, the structural parameters $k$, $rho$, $\sigma_l$ are chosen to be constants that reflect the desired level of mean reversion, curve intra pillar correlation, and long term vols. These can also be chosen according to observed market prices that are sensitive to them, e.g. swaptions, time spread options etc.
Calibration Sample results
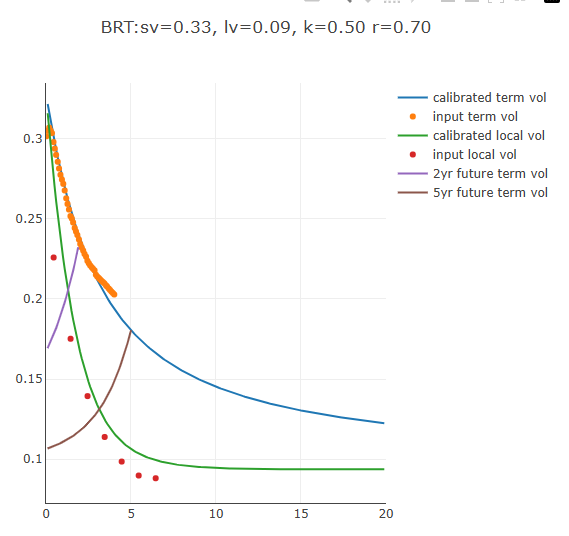
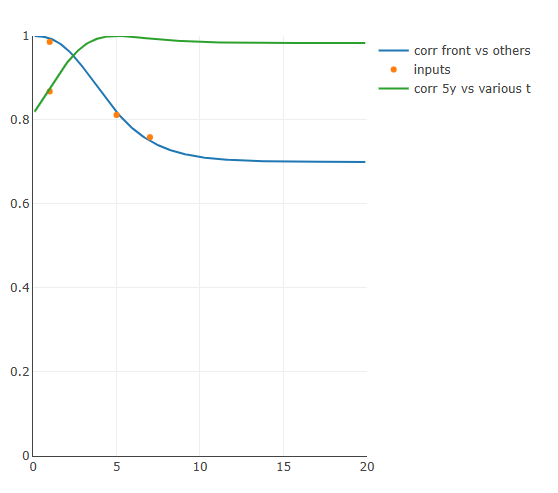
In the second step, we choose to calibrate a piecewise constant time dependent $\sigma_s(t)$ to the market implied volatilities of listed options. These are pseudo-realtime and are always recalibrated on the fly when the market vol changes. This is often used for oil contracts.
Alternatively, we can also fit a constant $\sigma(t,T_i)$ in time dimension, and a different one per futures maturity. This is often more suitable for gas contracts.
The forward cross covariance of two futures with different maturity $F_1(t,T_i)$, $F_2(t,T_j)$ and their own Gabillon model is
\[\int_{t_m}^{t_n} \left[ \begin{aligned} e^{-k_1 (T_i - t ) - k_2 ( T_j-2t )} \Sigma_{11}\\ +\left( 1 - e^{-k_1(T_i-t)}\right) \left( 1 - e^{-k_2(T_j-t)}\right) \Sigma_{22}\\ +e^{-k_1(T_i-t)} \left( 1- e^{-k_2(T_j-t)}\right) \Sigma_{12} \\ +e^{-k_2(T_j-t)}\left( 1- e^{-k_1(T_i-t)}\right) \Sigma_{21}\\ \end{aligned} \right] dt\] \[\begin{aligned} \text{Where}\\ \Sigma_{11} &= \sigma_s1(t,T_i) \sigma_{s2}(t,T_j) \rho(s1,s2)\\ \Sigma_{22} &= \sigma_{l1} \sigma_{l2} \rho(l1,l2)\\ \Sigma_{12} &= \sigma_{s1}(t,T_i)\sigma_{l2}\rho(s1,l2) \\ \Sigma_{21} &= \sigma_{s2}(t,T_j) \sigma_{l1}\rho(l1,s2)\\ \end{aligned}\]The integration result is:
\[\begin{aligned} & \frac{\Sigma_{11}}{k_1+k_2} \left( e^{-k_1(T_i -t_n) - k_2( T_j - t_n)} - e^{-k_1(T_i -t_m) -k_2( T_j - t_m)} \right ) \\ +& \Sigma_{22} \left( \begin{aligned} &t_n - t_m \\ -&\frac{1}{k_1} \left( e^{-k_1(T_i-t_n)}-e^{-k_1(T_i-t_m)} \right) -\frac{1}{k_2} \left( e^{-k_2(T_j-t_n)}-e^{-k_2(T_j-t_m)} \right) \\ +&\frac{1}{k_1+k_2} \left( e^{-k_1(T_i -t_n) -k_2 (T_j - t_n)} -e^{-k_1(T_i -t_m) -k_2 (T_j - t_m)} \right) \end{aligned} \right) \\ +&\Sigma_{12} \left( \frac{1}{k_1} \left(e^{-k_1(T_i-t_n)}-e^{-k_1(T_i-t_m)}\right) -\frac{1}{k_1+k_2} \left( e^{-k_1(T_i -t_n) -k_2(T_j - t_n)} -e^{-k_1(T_i -t_m) -k_2( T_j - t_m)} \right) \right) \\ +&\Sigma_{21} \left( \frac{1}{k_2} \left(e^{-k_2(T_j-t_n)}-e^{-k_2(T_j-t_m)}\right) -\frac{1}{k_1+k_2} \left( e^{-k_1(T_j -t_n) - k_2(T_i - t_n)} -e^{-k_1(T_j -t_m) - k_2(T_i - t_m)} \right) \right) \end{aligned}\]For a single Gabillon model, where
\(\rho_{s1,s2} = 1,\) \(\rho_{l1,l2} = 1,\) \(\rho_{s1,l2} = \rho_{s2,l1} = \rho,\)
the forward covariance of two futures with different maturities $F(t,T_i)$, $F(t,T_j)$ is reduced to
\[\begin{aligned} & \frac{\sigma_s(t_n,T_i)\sigma_s(t_n,T_j)}{2k} \left( e^{-k(T_i + T_j - 2t_n)} - e^{-k(T_i + T_j - 2t_m)} \right ) \\ +& \sigma^2_l \left ( t_n - t_m -\frac{1}{k}\left(e^{-k(T_i-t_n)}-e^{-k(T_i-t_m)} + e^{-k(T_j-t_n)}-e^{-k(T_j-t_m)}\right) + \frac{1}{2k} \left( e^{-k(T_i + T_j - 2t_n)} - e^{-k(T_i + T_j - 2t_m)} \right) \right) \\ +& \rho \sigma_s(t_n, T_i) \sigma_l \left ( \frac{1}{k}\left(e^{-k(T_i-t_n)}-e^{-k(T_i-t_m)}\right)- \frac{1}{2k} \left( e^{-k(T_i + T_j - 2t_n)} - e^{-k(T_i + T_j - 2t_m)} \right) \right) \\ +& \rho \sigma_s(t_n, T_j) \sigma_l \left ( \frac{1}{k}\left(e^{-k(T_j-t_n)}-e^{-k(T_j-t_m)}\right)- \frac{1}{2k} \left( e^{-k(T_j + T_i - 2t_n)} - e^{-k(T_j + T_i - 2t_m)} \right) \right) \end{aligned}\]When $i = j$, the forward variance of $F(t,T_i)$ is reduced to
\[\begin{aligned} &\frac{\sigma^2_s(t_n, T_i )}{2k} \left( e^{-2k(T_i - t_n)} - e^{-2k(T_i - t_m)} \right ) \\ +&\sigma^2_l \left ( t_n - t_m -\frac{2}{k}\left(e^{-k(T_i-t_n)}-e^{-k(T_i-t_m)}\right) + \frac{1}{2k} \left( e^{-2k(T_i - t_n)} - e^{-2k(T_i - t_m)} \right) \right) \\ +2&\rho \sigma_s( t_n, T_i ) \sigma_l \left ( \frac{1}{k} \left( e^{-k(T_i - t_n)} - e^{-k(T_i - t_m)} \right) - \frac{1}{2k} \left( e^{-2k(T_i - t_n)} - e^{-2k(T_i - t_m)} \right) \right) \end{aligned}\]